How You Can Benefit From Semantic Search
Updated 3.5.2023
Semantic enrichment gives data more meaning, making it more easily discoverable by both users and search engines.
Semantic search is changing the way digital marketing should be performed; gain the benefits of semantic search today! Google means to be an “Answer Engine,” trying to provide those who use it with the best results for their search queries. Accompanying Google’s move towards relevancy and semantic search is an adjustment for SEO’s. Most of us need to get better acquainted with semantic search technology and how to edit your Google Knowledge Graph. This article endeavors to be an introduction to the topic, to a few semantic experts, and to others who conduct technical SEO.
By studying Google semantically related keywords used in text, we see that when our content choices fit the natural use of language – visibility expands. Marketers who engage machine learning models for text analysis, disambiguation of subjects, keyword concepts, and classification are gaining semantic search advantages. In semantic search, the search results will return better snippets of information that will provide searchers a glimpse of a page’s content before clicking on a URL. Both visibility in Google’s Knowledge Graph and rich snippets assist user choices.
Is Learning Semantic Search Vital for SEOs in the 2020s?
Search engine technology is rapidly evolving, making semantic search essential for SEO. SEO professionals need to understand how keywords research has evolved, provide rich information that contextualizes those keywords, and firmly understand user intent. These things are vital for SEO in the era of semantic search, where machine learning, deep learning, and natural language processing are utilized by search engines to understand context and consumers better.
Semantic search refers to the capability of search engines to decipher the intent and contextual meaning of search phrases when serving content to people using the web. More sophisticated search algorithms now incorporate semantic search principles when matching the query to an answer and when ranking content. Semantic search is useful to provide deeper meaning to a searcher’s intent by evaluating the entity connections between sentences, words, possible contextual meanings, and the person’s search history. Let’s start with understanding se·man·tics [si-man-tiks], when used as a noun.
“The branch of linguistics that deals with the study of meaning, changes in meaning, and the principles that govern the relationship between sentences or words and their meanings.” – Collins English Dictionary
“Semantic search is a search, or a question, or an action that produces meaningful results even when the retrieved items contain none of the grey terms or the search involves no query text at all.” – Aaron Bradley
“Semantic search is Google’s growing ability to make associations between things in ways that come closer to how we humans make such connections.” – Mark Traphagen, of Stone Temple
“Semantic search seeks to improve search accuracy by understanding the searcher’s intent and the contextual meaning of terms as they appear in the searchable dataspace, whether on the Web or within a closed system, to generate more relevant results. Semantic search systems consider various points including context of search, location, intent, variation of words, synonyms, generalized and specialized queries, concept matching and natural language queries to provide personalized and relevant search results.” – wikipedia
Semantic rich content comprises writings that enhance the reader’s ability to gaining meaning and make sense of information that meets their search intent. It requires a structured strategy for web content creation and publication.
How did Semantic Search come about?
The Semantic Web’s origins lie in the extension of the World Wide Web. It offers a common and shared framework for data to be more widely reused and built upon. This is true across data scientists, applications, enterprises, and communities. The framework is also called an “ontology”, as it is commonly referred to in the field of information science. It partly relies on natural language process to gather facts and trusted information that eventually become a cataloged system of knowledge. To be more concise, semantic web structures and tags data combine entities in a manner that computers can read.
Is the use of semantic search growing?
Yes. George Anadiotis wrote for ZDNet that, “The application of graph processing and graph DBMSs will grow at 100 percent annually through 2022 to continuously accelerate data preparation and enable more complex and adaptive data science”. The July 31, 2019 Graph database reinvented: Dgraph Secures $11.5M to Pursue its Unique and Opinionated Path article discusses how graph data stores may easily model, explore and query data that contains complex interrelationships across data entity silos. but the need for specialized skills has limited their adoption to date. Graph analytics are growing in an effort to meet the needs of complex questions asked across explosively complex data.
What is Keyword Based Search?
Keyword-based search occurs when a user searches by using multiple variations of the same keyword. In multi-keyword semantics, coordinate matching may be used to identify as many relevant matches as possible. It attempts to capture search query similarities and trusted data documents.
Empowering searchers and search marketing professionals to access databases using simple keywords may offset the steep learning curve of mastering a structured query language. Semantic search expands search engines and digital marketers’ understanding of complex and possibly fast-evolving data schemas.
What does it take to Succeed in Semantics?
The increased use of semantic schemas are one of the most significant shifts in how we create, find, and consume content online. AI and well-structured data are revolutionizing SEO. While you have this amazing opportunity to get more relevant web traffic, reach a qualified audience and grow your business, its vital to avoid semantic schema drift.
It will take knowing what is the best schema to implement on each page, automating essential SEO tasks, and setting up experts who routinely monitor your semantic search efforts.
Use Semantic Density to Command a Lead in Conceptual Search
What is Conceptual Search?
A concept search (or conceptual search) is a robotic information retrieval method that is used to search repositories of big day computerized unstructured text (for example, scholarly journals, email, scientific literature, research, case studies, etc.) for information that is theoretically similar to the information provided in a search query. In other words, the viewpoints expressed in the information retrieved in response to a concept search query are related to the ideas encompassed in the text of the query.
If semantic search is a method of data searching technique where a search query aims to not only find keywords, then it can be used to establish the intent and contextual significance of the words a person is using for search.
A semantic search produces a precise result; whereas a concept search produces applicable and conceptual-related informational results.
Semantic density lets you provide support for queries in which concepts can be associated with a semantic scope such as general equivalence. Search algorithms are finding ways to be less disjointed in the process and are looking for exceptional web content that viewers want to read.
Search with an Initiative
News clips about big data are grabbing headlines at an increasing pace. Newcomers seek to understand it; marketers try to determine what is the best answer to offer with the help of semantic search terms. Using predictive data to understand user intent requires the ability to associate thought, analyses, abstract ideas, categorized, and incorporate findings correctly in relation to other datasets. Engagement and implementation of semantic technologies offer real value to businesses when the data output can be used for practical interpretations to understand better the company’s relationships with it’s clients.
Jarred McGinnis*, UK managing consultant of Ontotext, offers this take on semantic search; “Think of it as search with initiative: the results will be more targeted towards the goal of the search rather than being limited by the technical limitations of the person doing the searching.” Then read and implement strategic changes that are revealed in your SEO Reports.
Models Announced in 2018: TensorFlow Hub and Universal Sentence Encoder
Semantic textual similarity is meant to more easily understand text at the paragraph or even document level.
Expanding on the Universal Sentence Encoder model, Yinfei Yang, Software Engineer and Chris Tar, Google AI Engineering Manager, posted new models on TensorFlow Hub: the Universal Sentence Encoder – Large and Universal Sentence Encoder – Lite. They explained that they are pretraining to Tensorflow “models that return a semantic encoding for variable-length text inputs. The encodings can be used for semantic similarity measurement, relatedness, classification, or clustering of natural language text.”
The bigger model knows how to leverage the Transformer encoder and manages situations requiring high-precision semantic representations and the best model performance at the expense of speed and size. Google’s new Bard Generative AI is sure to make a big impact on search as we know it.
The May 17, 2018 article titled Advances in Semantic Textual Similarity explains that the Lite model is taught about a Sentence Piece vocabulary instead of words in order to drastically lower the vocabulary size, which is a major factor that makes up model size. It targets scenarios where memory and CPU resources are more measured, such as on-device or browser-based operations.
What benefits does a site gain from Semantic Search?
7 Benefits Digital Marketers May Obtain by Embracing Semantic Search Technologies
1. Site visitors are pleased when they can easily find answers.
2. Improvement of user experiences on-page (learn how to use Google’s Web Core Vitals Reports).
3. Business intelligence is enhanced.
4. Enterprises can build better relationships with their customers.
5. Semantic strategies encompass both earned and paid search.
6. GoogleBot finds it easier to understand your site and match queries to content.
7. The ability to use data for knowledge discovery
A Deeper Look at the Advantages of Semantically Enhanced Browsing
What are the benefits of semantic search?
1. Semantic Search Makes it Easier for Users to Find Answers
The chief benefit comes from additional semantic relations during query routing by search engines that offer better results. These relations provide a more interactive, conversational or dialogue-based search engine result pages or SERPs. Semantic search technologies may leverage Google Dataset search to allow people to track down the information by concept instead of by the limited match of a keyword or key phrase. This means that individuals can more effortlessly distinguish what will be on a page while making a choice as to which one to click through to. For example, semantic search makes it simple to decipher between searching for crane; the bird, crane, machinery used to lift heavy objects, and to crane, the verb, such as in “She had to crane her neck to see the car in her blind spot”. This difference has become a core part of what SEO is in the 2020s.
Search and search engines are all about what the user wants. That is why Google is releasing more in-depth Search Console Insights. The semantic approach is more successful in ensuring that users are not disappointed after arriving somewhere SERPs suggest. Those who entered the search query are free to decide which URL they want to explore and which they want to avoid based on what various rich snippets reveal. Users can mix traditional information retrieval (IR) queries and ontology-based ones. Push out your core content on Google Posts, which Google draws from when coming up with answers.
2. Semantic Enrichment can Improve User Experiences
A semantic approach to writing digital marketing messages spares readers from redundant and repetitive word choices. Most SEO’s set their sights on the most competitive traffic from Google. In the past, that may have been the best search engine optimization tactic, but Google algorithms are maturing, which creates opportunities to obtain more relevant search traffic. That can be better accomplished by semantically enriching your web content with solutions and links to sources that users want. Teodora Petkova, who offers a great course to learn semantic search, commented, “Links are to be understood and built with enrichment of understanding in mind.”
Related-content semantic tagging and linking is a way to offer users pathways to discovery to related content — whether related gems on your site or another highly relevant site that the user didn’t even know existed. By offering users’ the ability to read more content; a business can improve website metrics such as the number of page views and time on site. Empower the user with choices that they most likely want. Outbound links to supporting research and related topics may be what adds to their experience.
3. Semantic Enrichment Enhances Business Intelligence
Plan your future content so that it is more likely that your documents semantically enriched with metadata can expand your visibility online.
The method of using a semantic approach and structured data for content planning utilizes a data model to define the data. We focus on the value and the power of using structured data for business intelligence and offer case studies and how-tos. Read evidence that sites incorporating semantic benefits from this data science approach. Semantic metadata makes information retrieval a more worthwhile process.
If you prepare your site documents semantically, you can accrue higher benefits in Google Search. It’s much about removing barriers to Googler Crawler so it can focus on your top content. This plays a role for major enterprise semantic search improvements; advancements in the arena of technology search can highlight your genuine business benefits for the right buyer if your documents are prepared for a meaning searched by matching queries. Try this approach to gain an advantage for both earned and paid search.
4. Build Customer Relationships with Enterprise-strength Semantic Search
In semantic search, our digital content needs no longer hinge on a base system of recognizing keywords and returning exact word matches. Rather, by getting outside the boundaries of the speech terms, we can settle into a rut using, semantic keyword use helps companies grow customer relationships that matter by conversing in consumer’s manner of speech.
An SEO expert with a semantic approach can help companies identify, build and maintain their key customer relationships so that they can protect and grow their business.
Understanding semantics may also boost lead generation by being inclusive of valuable information which may be relevant but not tagged with the phrases used in users’ search. What may otherwise be lost content can become monetizable marketing.
The success of a business’s ongoing branding, search and digital identity hinges in part on the ability to be found in search engine result pages (SERPs). Knowing how to put your ideas, what you do, the questions that you answer, and the solutions you offer into findable and share-worthy words means better chances of getting found online. David Amerland says, “Companies that cannot successfully answer what they do fail to then understand how they can continue to do it in the face of change.”
5. Semantic Strategy Can Encompass Both Paid and Earned Search
Semantic strategy for semantic enrichment of both paid search and earned search has many benefits.
How Internet users find the content they want is progressively evolving towards a semantic “shape” to reach that information. One way to explain it is that the natural ordering and logic of web information has a semantic purpose and role. Business owners now have more ability to customize and control the text copy of your digital content.
Google offers users more than simply discovering information on a search topic — it’s now striving to order the web into a coherent flow of information; how topics, search themes, concepts, text, video, audio, and images are connected and associated to each other. Structured data markup is used to tie entities together.
Content added to a page should make the user experience richer and be tightly woven to that page’s unique purpose. When semantic keyword research supports how that content is conveyed, it is easier for more users to find the answers they are seeking. Semantic keyword strategy used in Google AdWords Ad Extension Structured Snippets can add to the value of your paid search.
While seeking semantic enrichment, marketers must factor cost, scalability, and accuracy into the decision process. To minimize associated risks, a well-thought-out semantic strategy will improve your probability of success.
6. Semantic Search makes it Easier for GoogleBot
“Semantic search requires a way to describe data conceptually and a way to search via these concepts”, according to Cambridge Semantics*.
Structured data may look to the human eye like a bunch of scrambled words, but for search engines, it unravels the words on a page. In the task of organizing information, it is critical for GoogleBot to find mechanisms to more precisely understand a web page’s content. By becoming more like authentic learning machines, search engines are interpreting content much faster and more accurately. These new technologies offer enormous benefits for search capabilities to be robust in terms of scalability, efficiency, and resilience to failure from indiscernible search queries. So by using schematics, we make this easier for them.
There are many workings that can help marketers accomplish business goals; adding semantic technology applications is one of the most relevant approaches to achieve them. In an article titled Keyword Research in 2016: Going Beyond Guesswork, Dr. Peter J. Meyers of Moz says: “We developed a Keyword Difficulty metric based on our authority metrics (Domain Authority and Page Authority). Page Authority (PA) is a constantly evolving metric that is designed to correlate with a page’s ability to rank on Google, based in large part on the page’s link profile. Keyword Difficulty (V1) used Page Authority in the middle-top of SERPs (the median PA, more or less) for a given keyword to approximate how hard that keyword would be to rank on.” We recommend using this tool to get ahead in your semantic search strategies.
A Semantically Enriched Digital Marketing Plan
When forming your semantic strategy, begin by answering the following questions:
• What user stories highlight your company’s premium products or services?
• Which business benefits and return on investment are most important in your business’s future?
• What web content do you need to tag and optimize? What pages best support your user needs? How can you replicate existing semantic successes across additional web pages?
• Which classification system will fit your needs best? Do standard taxonomies or thesauri exist that fit in your niche? How will you sustain your classification system?
• What are your best opportunities to display answers in Google’s Knowledge Graph?
Digital Marketers can Expect Future Semantic Search Enhancements
The International Press Telecommunications Council (IPTC) has recently been awarded a grant from the Google Digital News Initiative Innovation Fund to develop an additional, “multilingual open-source platform for rules-based classification of news content”. This should assist in helping “publishers to enhance their content with all sorts of metadata services, including enriched search, intelligent recommendations and precise analytics”, according to news updates from Aaron Bradley****, owner of the Google Semantic Search Marketing community.
The grant will go to improve the execution and exchange of information between content providers, intermediaries, and Internet users. Also, expect additions to semantic search for multilingual sites and advertising needs from schema.org. For marketers with clients serving international markets, Schema offers structured data markup currently only in English, but with hopes to expand more into additional languages that will aid when adding schema markup to your site for increased changes to show up in visually-appealing product carousels in SERPs. Metadata and semantic research is striving ardently to bridge the past, present, and future of metadata, data and semantic technologies. They power the featured snippets that produce visual search results.
6 Steps to Obtain Semantic Search’s Benefits
The semantic web is great at modeling and exploring entity relationships.
Once you have an understanding of how semantic search works conceptually — and how algorithms currently use it — you can take better advantage of leveraging semantic technologies.
1. Know your audience. Aggressively identify which channels your social audience participates in to find their interests, the questions they seek answers for, and their views on the topic. Then, write content that offers relevant and high-value solutions, or builds on those interests. Read between the lines to gather what they are really asking for and need, but may not know how to address.
2. Know how Google helps you find your audience. Google provides very clear and helpful usage guidelines. If you expect this search giant to deliver volumes of visitors to your website, then adhere closely to what Google says it needs you to do.
3. Add suitable semantic markup to your web pages. Choose the most closely woven markup vocabulary from schema.org. If you don’t find a perfect match, select the nearest category that you fit under. Start with Google’s own Structured Data Markup Helper or find your favorite code snippet generator. If your product markup validates with correct JSON-LD images sized, your products are more likely to be in evolving mobile Product Carousels.
4. Use only ethical SEO. Incorporate all standard aspects of SEO that use white hat tactics. Optimize page load times, the UX experience; build relational inbound links and domain authority.
5. Plan for mobile searches. More people prefer to search from mobile devices, meaning that sites that offer a feeble mobile experience compared to their competitors may find themselves lagging in mobile rankings.
Vast amounts of mobile data are generated and combined with mobile devices such as smartphones. Conduct market research to understand your mobile site visitors. Generally, mobile offers a user with a keyword-based full-text search (FTS) while searching for mobile data. However, FTS only processes the data analogous to the keywords given by users as results without deliberating a user’s query intention. To overcome this limitation, Google’s RankBrain algorithm uses a semantically enhanced keyword-based search method. To enable semantic search on mobile devices, a lightweight mobile ontology has become integrated. This “provides a better user experience than the conventional FTS and returns accurate search results in an acceptable response time”, according to an abstract from the Journal of Information Sciences**.
6. Integrate your entire web presence and marketing efforts. Don’t stop with on-page semantic search optimization. Social, SEO, SEM, PPC advertising, and Semantic Web/Semantic Computing need to liaise and coexist as a synergistically combined force. “Just as cross-pollination within a technology team will accelerate the pace of innovation, cross-pollination of these skills within a team will enable your team to keep pace with the necessary changes to attract your desired traffic to your website,” states Barbara Starr.
Businesses that embrace the concept of semantic search and implement it can gain a natural competitive edge. Semantic search experts offer businesses huge opportunities to increase visibility. Cutting-edge developments in machine learning continue to add to the value of semantic search. Semantic search technology relies on Classification (http://goo.gl/NrWsj5) and (http://goo.gl/LhkXuF) code Validation as two machine learning advancements.
It is challenging for many average SEO’s who are managing websites and who are overseeing their promotion to also add the full benefits of semantic search.
7. The ability to use data for knowledge discovery. It is only as gigantic as the ability to intelligently search through available data. Semantic search takes information retrieval to a more advanced level, empowering knowledge discovery like never before. Semantic search is emerging as a more trusted approach to querying data in the 2020s. It attempts to understand (meaning, to compute) the search intent and the context around a spoken or written query in order to retrieve the most pertinent entities that are related to the particular information request.
It is heavily used when search engines populate People Also Ask Boxes and Related Questions.
Semantic Search Improvements on Conventional Keyword-Based Search Results
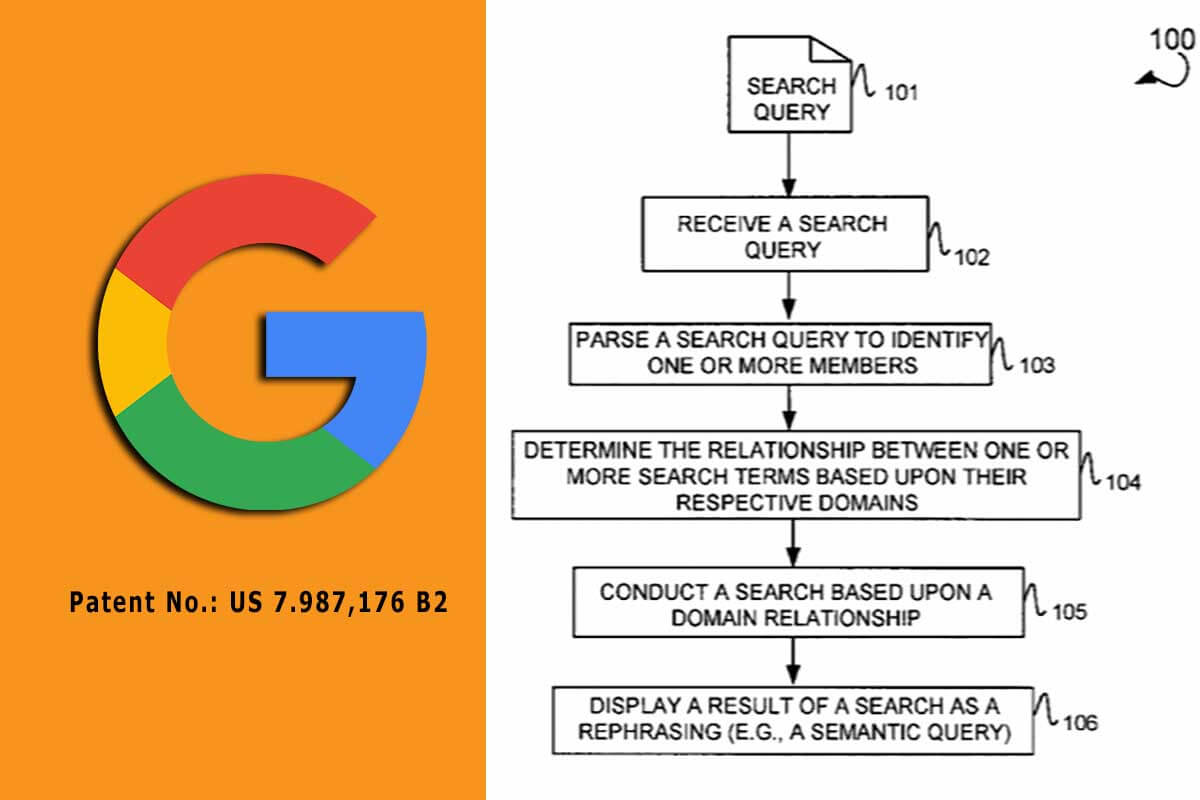
It can be a challenge for search engines to be able to address user search requests that could change.
Google seeks to analyze a new search query by parsing the search query to decipher first and second search terms and then assigns the first search term and the second search term to respective domains, each entity being a semantic category consisting of a set of entities of similar type.
When a person speaks for types a query to a search engine to ind an e-Commerce store, it may attempt to offer contexts arrived upon from other search queries from the same individual, the query associated with other information or query results from the same searcher, or other inputs related to that user to have better context to establish intent.
“In one embodiment, a method is illustrated including receiving a search query, parsing the search query to identify first and second search terms, determining a relationship between the first and second search terms based on their respective domain assignments, conducting a search based on the respective domain assignments, and displaying a result of the search based on the respective domain assignments, and the relationship between the first and second search terms, as at least one rephrasing of the search query.” – Google Patent
How to Measure Relevancy of Semantic Keywords Before Posting
A real benefit comes with your ability to garner long-tail traffic that comes from using search term phrases that more naturally occur in long-tail queries. Many times they are otherwise unexploited by not including all the related terms. By checking BEFORE you post a new piece of content to see what viewer interest level exists, you can avoid the “Your content is statistically irrelevant” issue. There are many ways to learn from big data how Google Alphabet uses semantics in search.
As well as using SEMrush and the new Moz Keyword Explorer, try the Alchemy API and Writer App**** to measure the relevancy of the website page content against a single semantic keyword phrase. In brief, this tool or several Chrome extension tools can analyze every word on the page to see if they are relevant or not to that pre-selected phrase. This can feel too geeky for the average non-technical user, but employing the skills of a true SEO expert, can make your content creations on-target for user wants. Then marketing it right may mean that you even go viral with it.
By putting in a strong effort upfront, you may be able to achieve a 99% relevancy score for your primary keywords. For example, if you wanted to do that for “Luxury Hotel”, you would want to make sure your homepage included words like suite, opulence, islands, boutique hotel, spa, resorts, private, leisure, safari getaways, premium guesthouse, package, indulge in extravagance, and fine dining accommodations. Use of semantically structured data will increase your chances of being awarded an answer box in a search. Representation and attempting to use them for variations is challenging at best. The semantic approach to writing or optimizing content for mobile advertising includes the work of deeper thinking to build relevant content that supports the topic. This form of content expansion enriches a blog post or organic landing page user experience, which ultimately increases your success.
The Longevity of Semantic Search
Search has merged into real-life entities that focus on user interactions, needs, and wants. Getting your business found today includes showing up in local map packs, especially for local service providers. Google’s deep learning experiments are using a structured approach that is better quantified and effective. “For AI search ranking to be a success, Google needs to transcend semantic markup…and will be an indelible tool for us in these early stages… more so that it ever has. A semantic understanding of your markups – let’s not forget that – and let’s actually focus on that.” said Mike Arnesen during the November 24, 2015, Semantic Search Marketing Open Forum
Semantic search involves a better means to recognize the way humans process and understand information. It helps facts be comprehensible to both humans and machines. Today, adding text to a page is a mere part of successfully reaching individuals using Google Search.
Much goes on behind the scenes for search engines to find relevant content to match user search queries. By incorporating text mining, semantic enrichment, and deep data integration tools, a stronger bridge can be made between digital text, meeting user expectations, and the knowledge businesses need in order to discover ways to reach new customers. Your messages either build your brand trust or tear it down.
Gerald Murphy sheds light on the path search engines have to take in a March 24, 2016 article titled, Are search engines ‘semantic’?******. While much is headed in the right direction, semantic technology has a long way to go. He explains that “Subject keywords are searched for semantically and today this is often just synonyms, a bit like an online thesaurus. For semantic search, the engine must deconstruct the whole query and reformulate it with variations, matching it with semantics, and construct sub-queries for each combination.”
Don’t Shelf it – Embrace Semantic Search NOW! Steps to Take to Engage Semantic Search
CURRENT CONTENT – Begin by ensuring that your current web pages consist of in-demand content and have the benefit of Classification that utilizes hashtags, and an Ontology structure that fits your business niche. Site thematic linking and theme concepts have become integrated more and more into SEO techniques.
• NEW WEEKLY CONTENT – Build and offer information that continues to offer your readers fresh content that interests them and supports your previous semantic search efforts. Semantic breadcrumb trails created by our digital footprints remain consistent and granular.
• ANNUAL MARKETING PLAN – No need to be daunted by semantic search; it practices are rational and straightforward; schedule them into your future digital marketing work.
If you are relatively new to discussions on semantics, you may be trying to access the merits and applications you need to glean for your website. For additional reading, a Merriam-Webster article titled It’s Time to Argue Semantics***** will help you step into the conversation. It covers the inception of semantics as early as the late 19th century as a technical word used in the field of semiotics, referring to such topics as the correlation between signs, words, and the concepts to which they refer.
Semantics relates to natural language. Consider if two or three individuals are caring on a conversation and seeking to cover it in detail, each person presents their opinion from a different angle on the same topic and uses similar but different words to explain it. Conversations are best when it is not about arguing over whose opinion is right; it is about benefiting from other’s take on the same matter. Likewise, there is little advantage in spending too much time and mental energy arguing semantics and unimportant detail; there is a tremendous benefit to relating better to our subject matter from the user’s viewpoint.
“Semantic technology makes everything connected to anything and helps to build smart eCommerce data through intricate models for representing information.” – Atanas Kiryakov CEO at Onotext
“Your (schema) markup must correlate with what is visible on the page. The information that you include in your markup must match the content that you’re displaying to visitors. My advice to others is to try to always stay away from gray areas so that you don’t have to worry about changing the markups later on or worse, getting penalized because of them.” – David Deering
“There is never a specific amount of data that can be enough when semantic search relies on constant judgments made based upon its ability to generalize and project.” – David Amberland
Hill Web Marketing offers services to advance your structured data for enhanced digital marketing results. Prices start at $1,500 per month (offer valid through July 31, 2024)
Why are semantic search mechanisms important?
Its purpose goes beyond the static dictionary meaning of a word or phrase to comprehend the intent of a searcher’s query within a specific context. Semantic search mechanisms leverage metadata to make it much easier to find Web pages based on advancing semantic criteria. Artificial intelligence learning from past results works to generate links between entities. A search engine may next be able to deduce the answer to a searcher’s query, rather than provide several links the traditional way. These mechanisms are meant to refine abilities to better provide the correct answer.
Conclusion
The web is an inter-connect series of real-life objects that transcends the limitation of words talking about web objects. The process of improving your site’s visibility in semantic search requires an on-going test and tweak application. It needs to be a part of every business’s marketing plan. This is where the metadata revealed becomes sufficiently semantic dense to generate fresh data that offers the benefit of key insights extracted from it. You can read answers to our most commonly asked search marketing FAQs.
When a group of individuals converses, they naturally use different word choices within the same topic. Request a consunmer behavorial analysis to gain insights on how to reach your audiences better. When writing for the web, by expanding on word choices, it is possible to encompass additional user searches and others conversing on the subject.
People tend to lose attention after a while if they hear the same thing stated in the same way too often. Likewise, web content is more readable and engaging when it puts solutions in multiple word phrase versions that a variety of readers can relate well to.
Hill Web Marketing is a Digital Marketing Agency that provides services in both earned and paid search to help businesses implement and manage semantic marketing across digital content. Our commitment is to provide you with improved marketing performance and user engagement. Does your site have a strong semantic structure? Are you using best practices in digital marketing for semantic search visibility? if you would like to partner in auditing your website content, together we can consider opportunities for growth for your business’s future.
Request a Website Audit for Semantic Opportunities
* http://www.computerweekly.com/blog/Data-Matters/Beyond-keywords-bringing-initiative-to-enterprise-search
** http://journals.sagepub.com/home/jis
*** https://www.cambridgesemantics.com/semantic-university/semantic-web-vs-semantic-technology
**** http://ntopic.org/writer.php
***** https://www.merriam-webster.com/words-at-play/lets-argue-semantics
****** https://www.searchenginewatch.com/2016/03/24/are-search-engines-semantic/
