Schema 3.2 brought us the option to add new structured data in the form of fact-check reviews.
When an individual either uses voice search or types a request for information on the Internet, search engines providing matches for the requested details, need options that are trustworthy. Adding fact check schema provides a SERP viewing that is capable of a pre-click demonstration that a page’s claim review requested has a valid source(s) behind it facts.
Being factual is one of the best ways to establish trust and credibility online. To add the Fact Check tag, webmasters have some rules to follow. Build your content around what users want, rely on trusted sources of information to back it up with facts, and be transparent as to where you gleaned them from. Customers, prospective buyers, and your fans come to know your digital reputation as a business that talks “straight truth” or stretches it.
While fact-checking articles gain no special ranking boost to move them to the “0” position or first page of results, the visibility can rocket your site in terms of clicks and conversions.
What is a “fact-check snippet”?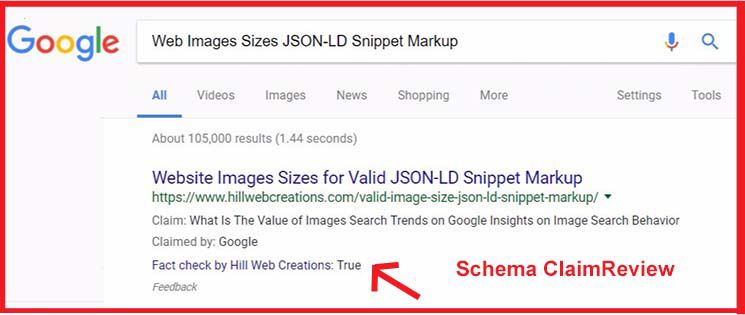
The snippets reference search words or phrases rather than being a tag for specific news. While seeking to offer valid sources of information, it includes a link to help readers form their own view on the topic.
ClaimReview is a type of source label that helps to inform search engines using machine learning about the content of your website and offers insights that help classify that content for rendering invisible SERPs. Google states: “We acknowledge the difficulty in characterizing different types of content in the rapidly changing publishing landscape, but we also hope to provide useful ways of helping users select what they want to read.”*
Fact Check is a label to help users evaluate content before clicking on a link in search engine result pages. The web page containing the Fact Check data provides a link to the original data itself to help viewers analyze it. Fact checks may provide the page quoted with a higher relevance than they might otherwise have.
Google does not determine what will always be true nor what is purely objective. The label offers additional information deemed to be from a reliable source. It is one way to assist those seeking more knowledge about the content. As long as the media has been around, it has been used to share opinions as well as fact, and to influence the public.
The Anti-Media Team defines Fact Check as “A rating system for the corporate media and by the media corporations”. The markup for fact-checking is called ClaimReview, and while pioneers of this work have now offered several examples, expect it to be expanded.
Fact Checking Using Natural Languaging Processing
In 2024, Google is increasing its focus on surfacing factual content. Apparently, too many sites state facts that aren’t even agreed upon the common public, much less a trusted brand entity. Google looks for entity facts that it use for searcher’s query matching. Today, we are using the Natural Languaging Processing for fact-checking. Google’s new Gemini LLM is much better at this.
If incorrect or misleading factual statements can be caught to a more satisfying degree, it may assist Veracity checks in search and generative AI composite models.
Simplifying how Publishers Use the Fact Check Tag
With the spread of false and misleading information online, Google is giving more ways for news publishers to let Internet users know what information is verified.
There are two aspects of fact checked content:
1. Business owners and publishers seeking to distribute accurate, fact-checked content via Google News and Google Search.
2. Users who want to consume trust worthy web content.
Erica Anderson, who is the Google Partnership’s manager, published an article title Making it easier for publishers to share fact check content on July 6, 2017. It states that “Expanding the use of the Fact Check tag to more news organizations around the world is important to raising the visibility of quality journalism on Google”. [1]
Surfacing Search Results with a Fact Check Tag
Trends in consumer behavior show that people want more factual content.
Users have long been a natural form of censorship. While it is unclear just yet how many searchers are noticing the FactClaim aspect, search engines have held long to the practice of surfacing search results they deem relevant and from a trusted source. Since few people click past the first few results, this form of structured data may help sites gain visibility in SERPs. The additional information may be implicative of censorship, but naturally, users are free to decide what to believe for themselves. Stating the original assertion along with comments that help to further define the claim is used to help readers deem the information as reliable or not.
While this form of Fact Check rich results is highly desirable, SEO professionals need to get it implemented correctly to avoid a spammy markup penalty.
Over the years, we saw Google News label its articles with certain tags such as “Opinion” or “In-depth” to help individuals select the type of content they prefer consuming. By adding “Fact Check” as one of these categories, site owners can gain Fact Checked recognition to relevant and trusted sources among its rich results in search. A page’s schema.org markup is quickly determined by machine learning, meaning that your page needs to evolve over time to take advantage of this coding opportunity and stay current with updated structured data guidelines. A full Technical SEO Audit is your best plan to assure correct use.
Timeline of Google’s Effort to Validate Fact Content
The Fact Check tag is not a new idea at Google. Google continues to highlight fact checks in search. Justin Kosslyn, a product manager at Jigsaw who partner with Google on this in 2011, was quoted as saying that he “started working on it (Fact Check Schema) but found that the necessary ‘building blocks’ to make it work were missing”.
Because JSON-LD markup has proved to increase online sales, you should use it to become more trusted when selling something online. In October 2016, Google News added the “Fact Check” label for articles that contain fact-based content. Today it has expanded and the schema has updated with new fields to populate. Originally, tagged articles found in the expanded story box on news.google.com, in the Google News, Weather iOS and Android apps were first available in the US and the UK.
In January 2017, a spokesperson at Google told the Daily Caller that mix-ups with labeling its news content were likely a problem with Google News’ algorithm and not a human error.
In May 2017, the search engine giant expanded a test fact-checking program globally. It’s a response to the spread of misinformation and criticism for how newer algorithms were returning fake facts and offensive information in some search queries.
As of July 10, 2017, in a parallel vein, the Data Act Information Model Schema has grown to over 400 data elements. The Digital Accountability and Transparency Act also recognize how critical it is to have trusted data sources and data standards are in place. ( https://fcw.com/articles/2017/06/30/whats-next-for-spending-data.aspx)
NOTE: In 2003 the website FactCheck.org was born. The Washington Post Fact Checker Checker’s ongoing database of the false and misleading claims and PolitiFact were launched in 2007.
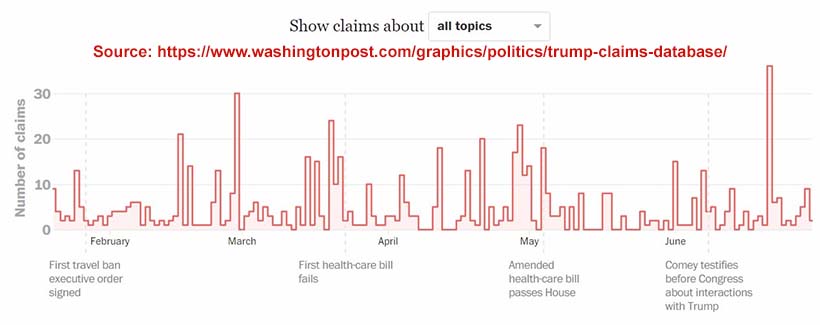 Fact-checking US politics
Fact-checking US politics
Our last U.S. presidential election was so extraordinary from a marketing perspective; it caused a ton of public concern that what talk stated as fact was indeed true and factual. Both Hillary Clinton and Donald Trump faced intense scrutiny as to if their claims were true or fake news. The Washington Post has a dedicated presence to provide its opinion as to the number of ongoing statements that President Trump has made and how many it considers as false and misleading claims.
A wide swag of differences among fact-checking organizations exist when it comes to determining true, false, and mixed fact check ratings, which we find key for mobile marketing and trust factors with micro-minute purchasing decisions. Due to variances in background, approaches, cultural, national, and organizational distinctions, fact checkers see things from a different perspective on truth. Currently, a committee of fact-checkers under the umbrella of the International Fact-Checking Network created a code of principles to establish a threshold of quality, consistency, and transparency among independent fact-checking organizations. Insurance fake news reports have also been on the rise. Service with a pre-claim review status helps protect public beliefs in our free speech society.
How Fact Check Schema Works
“If you have a web page that reviews a claim made by others, you can include a ClaimReview structured data element on your web page. This element enables Google Search results to show a summarized version of your Fact Check when your page appears in search results for that claim.” – Google Documentation
Imagine that someone claims on their website that if you buy their chocolate nut granola bar claiming there are no calories in it. Or that the current president of the United States won the election with more votes than any previous president, or that Google is the top social media platform, you would want to know that such a bold statement is factual. Adding trusted and factual content that is clearly sourced with correct schema will later show up in your Google Search Console Reports for any needed tested and editing.
The public has long been familiar with food and dietary supplement labels. This essential Schema markup type is similar to how the FDA strives to ensure that health claims, nutrient content claims, and structure or function claims are valid. Businesses have long used the media to state just about anything. Now the user experience includes a bit more assurance that they are reading from a reliable source with supporting links to the original source to make their own empowered opinion.
“No content is being removed or even ranked differently from what we can tell – so all the content is still there, unchanged, with an extra information box available for those who care to know how accurate the information is. Pretty simple,” states M. Luciano on Android Police. [2]
Whether or not someone is able to add information or context in order to mislead does not impact the actual fact itself. It can damage your brand entity reputation if you end up assessed as lacking credable, factual content.
Fact Check is Meant to Improve the User Experience
In September 2022, Google has removed the datePublished “recommended” property from the fact check structured data documentation.
We see the nested Organization structure data remains necessary for validity. People still want to know what business entity has stated the fact. Fact Check has been commonly thought of for just Google News sites, however, regular web search listing with special callouts (otherwise known as “rich snippets results“) work too.
It shows who has made a particular claim and the verdict, which can even be mixed. In the image example here, the claim is attributed to the internet at large and shows that some claim it is true and others say that it is false. Building trust is and important factor for your website. Inaccurate or false statements in you content may result in a significant loss of search traffic.
Google is serving up personalized search results. It seeks to match the intent of what the individual is searching for based on:
* The search history of the one conducting the query
* The most common searches of others search queries on the same topic
* The most common searches of others with similar search histories
The intent of offering this form of Schema is to provide users an at-a-glance method of determining whether or not a particular story has a solid basis of truth. Google is not trying to be identified as the Ministry of Truth here, but to help Internet users make quicker and better-supported decisions.
* Factual content may imporve your sites E-E-A-T and improve your changes of showing up in Google Top Stories and News Boxes.
How do I Gain Fact-Checked Snippet Results?
To match how users query the Internet, it helps to first prepare content that answers frequently asked questions. Then whether that answer surfaces in what Google calls a “fact-check snippet” depends on a number of factors, such as:
- 1. How the question is phrased.
- 2. The domain trust of the site referencing the fact.
- 3. If the topic had been fact-checked by someone taking part in Google’s program.
- 4. If the needed schema markup has been implemented on the page correctly.
If you are leveraging Generative AI to create answer content, you must validate that the facts included are indeed correct.
Who “Fact-checks” Sites using Fact-checked Schema”?
Since the whole point here is to separate fact from false statements, a rating system is in place to rank those using it not only from “true” to “false” but is also capable of identifying content that it finds “partly true” and “partly false.”
Anyone can request inclusion by filling out a simple form to be one, but Google alerts us that “Only publishers that are algorithmically determined to be an authoritative source of information will qualify for inclusion.”
Google has openly acknowledged that different publishers and users may draw different conclusions about the validity of a news story or Fact Check Statement but believes that the feature helps people gather a “degree of consensus” on a particular topic. From our experience, we recommend making double sure that any medical facts someone might search for or financial statements are well documented and from a trusted source.
Currently, how the ClaimReview field for URL of claims can be formed:
- You can use a claim from a tweet, a person’s quote in a speech, an encyclopedia, an article, etc.
- Each fact claim may be repeated in multiple sources and may also have an origin, where the claim was originally published.
- The fact-checker examines an instance (or repeater or cheerleader) of the stated claim, which is modeled inside
itemReviewed. Note that upon researching it, one often finds it is not the original instance of the claim, but rather the most recognized individual who’s making the claim
We recommend supporting your content that demonstrates niche expertise with factual statistics.
Countries were Worry About Fake News is a Big Deal
While more U.S. citizens are seeking factual validation, Germans are the people who feel the most positive in general and worry less about the fake content they read on the Internet. A BBC survey found that a smallish 14 percent are super perturbed by content that may be ranked as fake. Another 33 percent are somewhat worried. This means that while 47 percent overall are worried to some measure, it’s a low figure compared to how worried people in other countries reportedly are. In the USA, 53% are worried about fake news. In Brazil, a higher percentage of individuals find it upsetting: 92 percent are worried about what’s real and what’s fake.
So let’s dive into Google’s guidelines to address the matter.
Google Fact Check Guidelines
Google provides several clear guidelines for this specific type of fact-checking schema markup that are added to general schema markup requirements. [3]
- Fact checks associated with news articles can be shown in either News results or the combined search results view; all other fact checks can appear only in combined search results view.
- Fact checks of a news claim must meet the News Publisher criteria for fact checks.
- Fact checks are not guaranteed to be shown: inclusion of fact check elements in Google Search results is determined programmatically. Fact check elements are scored based on a programmatic ranking of the site. Sites are evaluated in a process similar to page ranking: if the site ranking is high enough, the fact check element can be displayed in search results along with your page. The entire process is conducted programmatically; human intervention only occurs when user feedback is filed as violating the Google News Publisher criteria for fact check, general guidelines for structured data, or when the publisher (whether or not a news site) does not meet standards for accountability and transparency, readability or site misrepresentation.
- A single page can host multiple
ClaimReviewelements, each for a separate claim. - If different reviewers on the page check the same fact, you can include a separate
ClaimReviewelement for each reviewer’s analysis (see below). - The page hosting the
ClaimReviewelement must have at least a brief summary of the fact check and the evaluation, if not the full text. - You should host a specific
ClaimReviewon only one page on your site. Do not repeat the same fact check on multiple pages, unless they are variations of the same page (for example, you can post the sameClaimReviewon the mobile and desktop
versions of a page).
Future ClaimReview Integrations of new Claim Type
Dan Brickley posted a great documentation on GitHub of how all these constructs fit into the following key concepts:
ClaimReview-based factcheck markup defines a structure that corresponds to the kind of information included in many fact-checking pages. The fundamental notion is a ClaimReview has an author (schema.org/author), which is typically an Organization (schema.org/Organization) (i.e. the fact checking organization or publisher), but could also be a Person (schema.org/Person).
The claimReviewed (schema.org/claimReviewed) property of a ClaimReview (schema.org/ClaimReview) summarizes the claim being reviewed. This may include clarifications of the original wording to address intelligibility, civility, context or brevity, and can include translations.
This value of the claimReviewed (schema.org/claimReviewed) property is typically a simple textual string (but could be a Claim (schema.org/Claim) with a text (schema.org/text) property, although this is not encouraged). The itemReviewed (schema.org/itemReviewed) property of ClaimReview (schema.org/ClaimReview) indicates specific manifestations of the claim being reviewed. This can either be a Claim (schema.org/Claim) [preferred] or [historically] a CreativeWork (schema.org/CreativeWork) within which the claim is described or reported.
The value of itemReviewed (chema.org/itemReviewed) (preferably a Claim (schema.org/Claim) to avoid ambiguity) has an author (schema.org author), which is a Person (schema.org/Person) or Organization (schema.org/Organization) that has made the claim.
A Claim (schema.org/Claim) can be associated with a CreativeWork (schema.org/CreativeWork) it occurs in, using the appearance (schema.org/appearance) or firstAppearance (schema.org/firstAppearance)properties. This is preferable to describing appearances using itemReviewed (schema.org/itemReviewed) as it distinguishes more explicitly between the author (schema.org/author) of the Claim (schema.org/Claim) versus author (schema.org/author) of materials discussing those claims.
The reviewRating (schema.org/reviewRating) property of the ClaimReview (schema.org/ClaimReview) indicates a Rating (schema.org/Rating) of the claim. A rating can be summarized textually with a alternateName (schema.org/alternateName) property, and with a numerical rating on a scale from worstValue (schema.org/worstValue) (lowest) to bestValue (schema.org/bestValue) (highest).
The author (schema.org/author) (or creator (schema.org/creator), publisher (schema.org/publisher) of a ClaimReview (schema.org/ClaimReview), or of a Claim (schema.org/Claim), or CreativeWork (schema.org/CreativeWork), can be either an Organization (schema.org/Organization) or Person (schema.org/Person)
How to Surface Your Fact-Based Content in Google SERPs
Chatbots can serve your factual answers to user’s questions.
Links are now just one of the top web ranking factors. In the proliferation of web content, becoming a source for trusted information on a topic of interest to your clients and prospective buyers means that you are successfully putting the user experience first.
One of the leading 2019 search trends is the user’s demand for factual content. ClaimReview Schema markup is especially important in the age of Hummingbird and RankBrain to help search engines interpret your pages to fit the context of a search query. We are on alert for updates in this code application. According to GitHub, “At a high level, claimReviewed, claimUrl, claimUrilOriginal are all attributes of ClaimReview, it seems to be pretty well organized as a unit”.
Find trusted information on which sources agree before adding claimreview markup.
Understand the degree of interest in your topic and the level of trust needed to encourage followers and shares. Solid research will help to find the consensus around a particular claim to solidify if it is indeed factual. Computer science has a tough job shorting out the false claims that business make on their website to sound trustworthy. Google Data Search is surfacing new datasets that can be sourced to back up your claims.
Your SEO is only as effective as it is correct and current. Make sure you keep reviewing your FactCheck schema for changes and making errors as soon as possible. This will protect your domain from schema markup drift.
“Everybody deserves to have access to reliable, impartial, and accurate information. In the maelstrom of 24-hour news and social media, this isn’t always easy to find. But thanks to Google News, people who have never even heard of Full Fact will be able to find the unbiased information they need to make up their own minds and feel confident in the decisions they make.” – fullfact.org
“We’re excited to see the growth of the Fact Check community and to shine a light on its efforts to divine fact from fiction, wisdom from spin.” – Richard Gingras, Head of Google News
Google’s Technical guidelines Updated 2021-11-22
- To be eligible for the single fact check rich result, a page must only have one
ClaimReviewelement. If you add multipleClaimReviewelements per page, the page won’t be eligible for the single fact check rich result. (Previously, it said: “A single page can host multiple ClaimReivew elements, each for a seperate claim.”) - The page hosting the
ClaimReviewelement must have at least a brief summary of the fact check and the evaluation, if not the full text. - A specific
ClaimReviewmust only be on one page on your site. Do not repeat the same fact check on multiple pages, unless they are variations of the same page (for example, you can post the sameClaimReviewon the mobile and desktop versions of a page). - If your website aggregates fact-check articles, ensure that all articles match the criteria and that you provide an open and publicly available list of all fact-check websites you aggregate.
| Required properties | |
|---|---|
claimReviewed |
A short summary of the claim being evaluated. Try to keep this less than 75 characters |
reviewRating |
The assessment of the claim. This object supports both a numeric and a textual assessment. Different fact-checking projects have a variety of rating schemes which can have subtle differences,
For more information, see Rating. |
url |
Link to the page hosting the full article of the fact check. The domain of this URL value must be the same domain as, or a subdomain of, the |
 Hill Web Marketing’s owner, Jeannie Hill, is passionate to help clients move thier business forward online by implementing fact check schema to build trust and accuracy. We endeavor to provide detailed schema code, search engine optimization, and cutting-edge machine learning technology..
Hill Web Marketing’s owner, Jeannie Hill, is passionate to help clients move thier business forward online by implementing fact check schema to build trust and accuracy. We endeavor to provide detailed schema code, search engine optimization, and cutting-edge machine learning technology.. Residing in Minneapolis, Minnesota, we provide both on-site and remote digital marketing services.
Some question if this new feature may result in hyperpartisan entities of any passionate persuasion could post “fact check” statements that are not really well-suited as fact checks at all. Read more about the benefits and typical costs of adding schema.
You can use natural language process tools for fact checking. As well, new AI prompt engineering can be very helpful to check factual sources and to add your facutal content to your Knowledge Graph.
SUMMARY
While any site can mark up its content with fact-checking schema, transparency and your long-term trust factor will be attributed to your sources and methods of fact-checking.
As with product schema, image schema implementation, and others, proven veracity and correctness will prove stable over the updates that are sure to come. Testing and implementing Fact Check Schema on your Website is technical SEO and extensible. Hill Web Marketing provides professional digital marketing services to implement fact check Schema to build online credibility. ClaimReview can be used to build credibity for your Minneapolis business. Services begin at 2,500.00 (Offer ends 2024-07-31).
Resources:
[1] https://blog.google/outreach-initiatives/google-news-initiative/making-it-easier-publishers-share-fact-check-content/
[2] http://www.androidpolice.com/2017/04/07/fact-check-goes-global-search-google-news-results/
[3] https://developers.google.com/search/docs/appearance/structured-data/factcheck
For help to align your search marketing strategies for the future and correctly implement Fact Checking Schema to an otherwise ambiguous web page, call Hill Web Creations today: 651-206-2410 Schema Site Audit
* http://www.androidpolice.com/2017/04/07/fact-check-goes-global-search-google-news-results/
